Generic Name/API: Leucovorin calcium
Brand name: Leucosad
Marketed By: Sadaya Healthcare Pvt Ltd
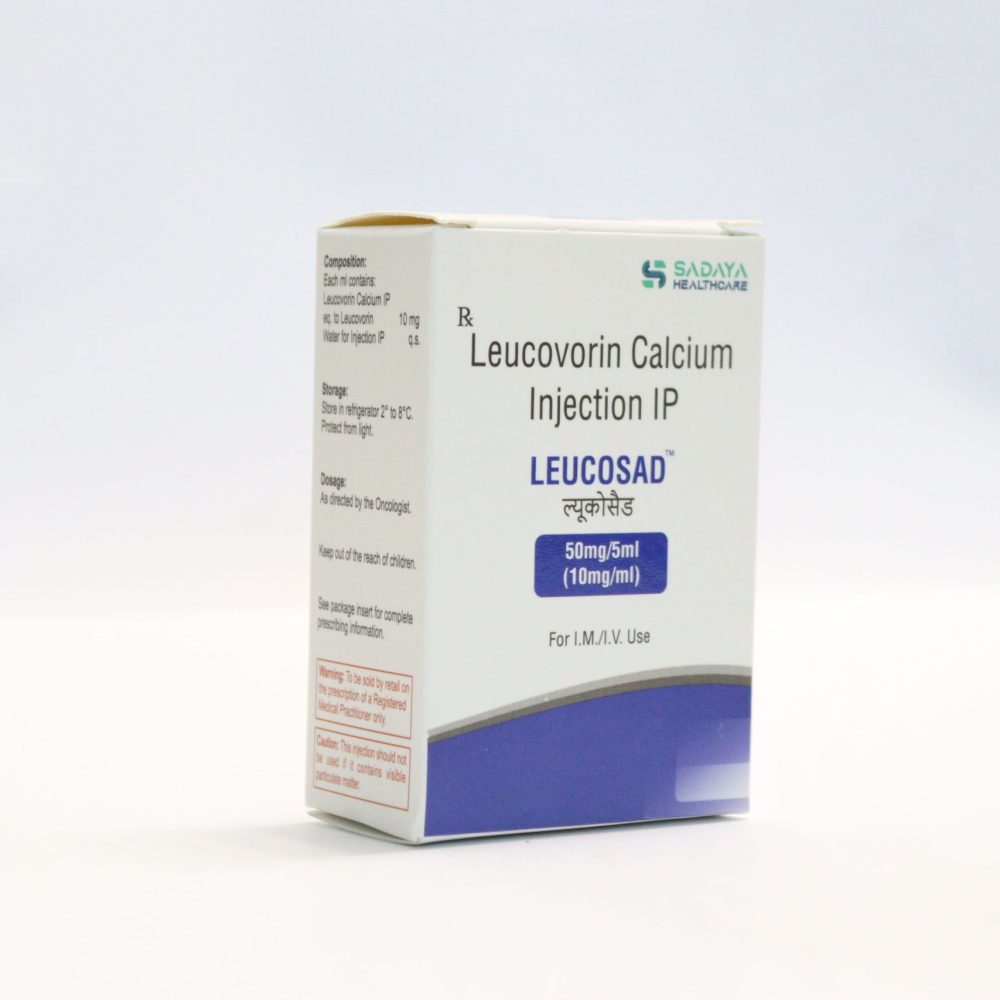
Strength: 10mg/ml
Packaging: 50mg/5mL (10mg/mL) Leucovorin Calcium + Water for Injection
Pack size: Single use vials
Storage: Store in the refrigerator 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F)
More Information click here LEUCOSAD_DOSAGE_PRODUCT
Product USP:
Leucovorin is a clinically proven, FDA approved optimized folate support that enhances the efficacy of chemotherapy and manages toxicity in high dose methotrexate treatments, preventing severe hematological complications including anemia.
Indication:
- Leucovorin, an FDA-approved folate analog, is used as a rescue therapy after high-dose
methotrexate treatment for osteosarcoma or accidental overdose of folic acid antagonists.
It pharmacologically classifies as a detoxifying agent for antineoplastic drugs.
It is an essential cofactor in the body and helps mitigate the toxic effects of drugs like
methotrexate, which inhibit dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), potentially causing serious blood
disorders such as thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and anemia.
It is also used to treat megaloblastic anemia due to folic acid deficiency when oral folic acid
intake is not possible
- In oncology, leucovorin is frequently combined with 5-fluorouracil to enhance its effectiveness
and prolong survival in patients with advanced colorectal cancer.
Additionally, it is used to manage methotrexate toxicity, which can cause symptoms like nausea,
vomiting, diarrhea, stomatitis, mucositis, esophagitis, liver enzyme elevation, rash, renal failure,
myelosuppression, acute lung injury, hypotension, tachycardia, and neurological dysfunction.
Leucovorin is used as a neoadjuvant treatment for bladder, advanced esophageal, gastric, and
pancreatic cancers.
Mode of administration:
- Intravenous or intramuscular administration
- Mechanism of action
Leucovorin, an active folic acid metabolite, counteracts folic acid antagonists like methotrexate by
displacing it from intracellular sites and restoring folate for DNA/RNA synthesis. In methanol
toxicity, it provides tetrahydrofolate to aid in formic acid elimination. It also enhances fluorouracil’s
activity by stabilizing its active metabolite’s bond with thymidylate synthetase.
Adverse reactions
- Anaphylactic reactions and urticaria have occurred in patients undergoing oral and parenteral
leucovorin therapy. - Leucovorin enhances the toxicity of 5-fluorouracil.
- Leucovorin has counteractive effects when used with antiepileptics such as primidone,
phenobarbital, and phenytoin. (See DRUG INTERACTIONS) - Higher rates of ineffective or failed treatment are reported when leucovorin is used
concomitantly with sulfa drugs to treat Pneumocystis jirovecii.
Recommended dosage :
- In the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer, Either of the following two regimens is
recommended: - Leucovorin is administered at 200 mg/m2 by slow intravenous injection over a minimum of 3
minutes, followed by 5-fluorouracil at 370 mg/m2 by intravenous injection. - Leucovorin is administered at 20 mg/m2 by intravenous injection followed by 5-fluorouracil at
425 mg/m2 by intravenous injection.
Infusion: not to exceed 160 mg/min
Warnings & Precautions
- Accidental overdose of folic acid antagonists can be treated with intravenous leucovorin
administration. As the time interval between antifolate administration (e.g., methotrexate) and
leucovorin rescue increases, leucovorin’s effectiveness decreases.
The administration should be strictly intravenous, as using intrathecal route may be extremely
lethal and harmful. - Appropriate dose and duration of the treatment may be suggested post serum methotrexate
concentration monitoring. The dosage or the duration of the treatment may be increased in
cases like third space fluid accumulation ( eg. ascites, pleural effusion), renal insufficiency or
inadequate hydration, i.e cases where methotrexate elimination from body by excretion is
delayed. - Doses higher than those recommended for oral use must be given intravenously.
The dosage of 5-fluorouracil must be lowered below the standard dosage when used in
combination with leucovorin as leucovorin enhances its toxicity when used in combination in
advanced colorectal cancer treatment. - Although the toxicities observed in patients treated with the combination of leucovorin plus
5-fluorouracil are qualitatively similar to those observed in patients treated with 5-fluorouracil
alone, gastrointestinal toxicities (particularly stomatitis and diarrhea) are observed more
commonly and may be more severe and of prolonged duration in patients treated with the
combination. - Patient and physician should be mindful of the patient’s allergies to the ingredients.
In case of certain types of anemia(megaloblastic anemia, pernicious anemia), leucovorin is not
prescribable. Blood tests should be done before administration of leucovorin in such cases.
Common Side Effects:
- Severe allergic reactions
- Breathing problems or wheezing
- Racing heart
- Fever or general ill feeling
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue, or throat
- Trouble swallowing or throat tightness
- Itching, skin rash, or pale red bumps on the
- skin called hives
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness, feeling lightheaded, or fainting
- Stomach cramps
- Joint pain
Storage and Handling:
- Store in the refrigerator 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F). Protect from light. Discard unused portions.
- Retain in carton until time of use.
About Pharmacology
- Absorption: Leucovorin is rapidly absorbed after oral administration.
- Apparent bioavailability: – 97% for 25 mg – 75% for 50 mg – 37% for 100 mg
Peak plasma time: Oral (PO): 2 hours, Intravenous (IV) as folate: 10 minutes, as
tetrahydrofolate: 1 hour - Distribution: Distributed to all body tissues, predominantly in the liver.
Metabolism:
- Primarily metabolized in the liver and intestinal mucosa.
- Rapidly converted to tetrahydrofolate (THF) derivatives, with the major metabolite
being 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-methyl-THF). - Leucovorin is also converted to 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate, which stabilize
luorodeoxyridylic acid binding to thymidylate synthase, enhancing enzyme inhibition. - Excretion: Primarily excreted in urine (80-90%), a smaller portion is excreted in feces (5-8%).
Elimination & Half-life : Half-life elimination: 4-8 hours. - Terminal half-life of total reduced folates: 6.2 hours.
Toxicity –
- LD50: >8000 mg/kg (oral in rats).
- Excessive leucovorin may counteract the effects of folic acid antagonists used in chemotherapy due to enhanced toxicity.
Drug interactions :
- Folic acid in large amounts may counteract the antiepileptic effect of phenobarbital, phenytoin
and primidone, and increase the frequency of seizures in susceptible pediatric patients. - High doses of leucovorin may reduce the efficacy of intrathecally administered methotrexate to treat cancer. Leucovorin may enhance the toxicity of 5-fluorouracil. Dermatologic,
- gastrointestinal and central nervous system toxicity is most commonly reported.
Healthcare professionals should be intimidated if the patient being considered leucovorin
treatment is under any medication from the list below. The dosage of one or both of the
medicines will be adjusted by the doctor, based on the net effect and balance between negative
and positive effects of such a combined therapy: - Capecitabine
- Doxifluridine
- Fluorouracil
- Antibiotics (sulfa drugs) like
- Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim
- Tegafur
Some drug drug interactions cause increased risk of side effects, but the benefit outweighs this
drawback and hence the doctor may still prescribe the combination and adjust the dosage. - Glucarpidase
- Phenobarbital and Primidone are used as antiepileptic drugs to prevent six=zures. Leucovoorin
may have counteracting effects, increasing the frequency of seizures.
This may not be a complete list of medicines that can interact with leucovorin. Always check with your
healthcare provider. - Other interactions include possible reactions with food, alcohol, tobacco and supplements.
The healthcare provider should be informed about any prescription or over the counter
medicines, vitamin or mineral supplements, herbal products or other supplements the patient
may be using.
Important:
- Prior to initiating treatment, it is essential to engage in a comprehensive discussion with your healthcare provider regarding any current medications, medical conditions, pregnancy status, or intentions for breastfeeding. This dialogue allows your doctor to evaluate potential drug interactions and customize a treatment regimen that aligns with your specific requirements, emphasizing your safety and health. For personalized information and guidance, it is recommended to seek further
clarification and advice from your doctor. The medicine is to be administered by a healthcare professional in a proper hospital setting, in the form of an injection (strictly intravenous administration). Intrathecal administration is strongly prohibited.
The dose, route of administration, and frequency will be decided by the physician based on your
diagnosis.
Use in Specific Population
General Considerations
- The risks and benefits of leucovorin should be carefully weighed before use.
Patients should inform their healthcare provider of any allergies to medications, foods, dyes, preservatives, or animals.
Pediatric Use:
- In children with seizure disorders, leucovorin may increase seizure frequency. (See DRUG
INTERACTIONS). Hence, use in pediatric patients should be closely monitored.
Geriatric Use:
- No significant differences in safety or efficacy have been established so far between elderly and
younger adults in clinical studies with over 65 and younger patients. Renal function should be
monitored, as leucovorin is excreted by the kidneys and elderly patients are more likely to have
impaired renal function due to toxic reactions.
Other clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and
younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older patients cannot be ruled out.
Pregnancy (Category C)
- Teratogenic effects unknown as adequate animal reproduction studies have not been conducted.
There is no confirmed risk to fetal development, but leucovorin should only be used during
pregnancy if clearly necessary.
Breastfeeding
- There is a lack of sufficient evidence establishing the secretion of leucovorin in human milk.
Since many drugs pass into breast milk, caution is advised, and potential benefits should be
weighed against potential risks.
Patients with Renal Impairment
- As leucovorin is primarily excreted by the kidneys, patients with renal dysfunction may be at
higher risk of toxicity.
Dose adjustments and renal function monitoring may be necessary.
Contraindications
- Leucosad is not the correct therapy for patients with underlying issues like pernicious anemia and other megaloblastic anemias caused due to Vitamin B12 deficiency. A hematologic remission may occur while neurologic manifestations continue to progress.
CT results and efficacy wrt comparator drug
- A Mayo/NCCTG trial in metastatic colorectal cancer compared leucovorin (LV) and
5-fluorouracil (5-FU) regimens. Low-dose LV (20 mg/m²) + 5-FU (425 mg/m²) had the
highest response rate (43%) and significantly improved weight gain, symptom relief, and
performance status.
A second trial tested sequential methotrexate (MTX), 5-FU, and LV, showing a lower response
rate (14%) compared to LV + 5-FU regimens.


FAQ
What is leucosad used for ?
Leucosad helps in detoxifying methotrexate in patients undergoing chemotherapy for cancer, especially colorectal cancer.
How should patients be monitored post administration of leucosad?
Patients should be checked for third space fluid accumulation ( eg. ascites, pleural effusion), renal insufficiency or inadequate hydration. - In patients over 65 years, renal function should be monitored, as elderly patients are more likely to have impaired renal function due to toxic reactions.
How is leuosad administered?
IV/IM
What are the common adverse reactions associated with leucosad?
(See adverse reactions).
What is the price of leucosad in India?
Rs. 321
What all should be avoided while in treatment with leucosad?
Alcohol and tobacco are generally strongly prohibited.
Other than that, some drug interactions
having lethal effects when used with
leucovorin should be considered before adjusting dosage.
Drugs like capecitabine, doxifluridine, fluorouracil, antibiotics (sulfa drugs) like
sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim and tegafur are such drugs .
Also leucovorin has a
counteracting effect on antiepileptics and hence whether to use such drugs or not or adjust
dosage should be checked for.
References:
1) Leucovorin - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf
2) LEUCOVORIN CALCIUM INJECTION Label

Written By
Ashwini Priya
Medical Content Writer

Approved By
Dr Anchal
Medical Advisor